Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2023-023, 99 Pages, 2024/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human Resource Development Related to Remote Control Technology for Monitoring Inside RPV Pedestal during Retrieval of Fuel Debris" conducted in FY2022. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2022, each system was improved and expanded toward the final year, and verification experiments were conducted in simulated environments.
Miura, Yasufumi*; Suzuki, Kenji*; Morooka, Satoshi; Shobu, Takahisa
Quantum Beam Science (Internet), 8(1), p.1_1 - 1_14, 2024/03
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2022 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2023-022, 93 Pages, 2023/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2022. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple
, and X-rays" conducted from FY2020 to FY2022. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple  -ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereinafter referred to as "SDM") was developed. In the research in 2022, we developed a code that handles measurement data of LSC, singles Ge, and 2D spectra (multiple
-ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereinafter referred to as "SDM") was developed. In the research in 2022, we developed a code that handles measurement data of LSC, singles Ge, and 2D spectra (multiple  ). In addition, to develop an integrated database, spectral data of 40 nuclides were obtained by actual measurements and simulation calculations.
). In addition, to develop an integrated database, spectral data of 40 nuclides were obtained by actual measurements and simulation calculations.
Suzuki, Seiya; Nemoto, Yoshihiro*; Shiiki, Natsumi*; Nakayama, Yoshiko*; Takeguchi, Masaki*
Annalen der Physik, 535(9), p.2300122_1 - 2300122_12, 2023/09
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Physics, Multidisciplinary)Maeda, Makoto; Segawa, Mariko; Toh, Yosuke; Endo, Shunsuke; Nakamura, Shoji; Kimura, Atsushi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(8), p.2995 - 2999, 2023/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)Iwase, Hiroki*; Akamatsu, Masaaki*; Inamura, Yasuhiro; Sakaguchi, Yoshifumi*; Morikawa, Toshiaki*; Kasai, Satoshi*; Ouchi, Keiichi*; Kobayashi, Kazuki*; Sakai, Hideki*
Journal of Applied Crystallography, 56(1), p.110 - 115, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:85.44(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)With the increasing importance of light-responsive materials, it is vital to analyze the relationship between function and structural changes induced by light irradiation. Small-angle scattering (SAS) is effective for such structural analysis. However, quantitatively capturing local molecular structure formation and molecular reactions at a scale of less than 1 nm via SAS is difficult. In this study, to analyze the structure of non-equilibrium phenomena in light-responsive materials, a new sample environment has been developed for a time-of-flight small- and wide-angle neutron scattering instrument (TAIKAN), comprising a UV-Vis irradiation system, UV-Vis absorption measurement equipment and photodetector. Simultaneous measurement of small-angle neutron scattering and UV-Vis absorption was achieved. This system was used to demonstrate the in situ observation of UV-Vis irradiation-induced structural change of micelles formed by a light-responsive surfactant sample in an aqueous solution.
Hirano, Tatsumi*; Maeda, Takehiro*; Murata, Tetsuyuki*; Yamaki, Takahiro*; Matsubara, Eiichiro*; Shobu, Takahisa; Shiro, Ayumi*; Yasuda, Ryo*; Takamatsu, Daiko*
SPring-8/SACLA Riyo Kenkyu Seikashu (Internet), 11(1), p.49 - 57, 2023/02
Togawa, Orihiko; Okura, Takehisa; Kimura, Masanori
JAEA-Review 2022-049, 76 Pages, 2023/01
Before construction and after operation of nuclear facilities, environmental consequence assessments are conducted for normal operation and an emergency. These assessments mainly aim at confirming safety for the public around the facilities and producing relief for them. Environmental consequence assessments are carried out using observations/ measurements by environmental monitoring and/or model predictions by calculation models, sometimes using either of which and at other times using both them, according to the situations and necessities. First, this report investigates methods, roles, merits/demerits and relationship between observations/measurements and model predictions which are used for environmental consequence assessments of nuclear facilities, especially holding up a spent nuclear fuel reprocessing plant at Rokkasho, Aomori as an example. Next, it explains representative examples of utilization of data on observations/measurements and results on model predictions, and considers points of attention at using them. Finally, the report describes future direction, for example, improvements of observations/measurements and model predictions, and fusion of both them.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tokyo Institute of Technology*
JAEA-Review 2022-043, 52 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2021, this report summarizes the research results of the "Fuel debris criticality analysis technology using non-contact measurement method" conducted in FY2021. The purpose of research was to improve the fuel debris criticality analysis technology using non-contact measurement method by the development of the fuel debris criticality characteristics measurement system and the multi-region integral kinetic analysis code. It was performed by Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech), National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST), and National Research Nuclear University (MEPhI) as the first year of four years research project. For the criticality characteristic measurement systems to be developed by the Japanese and Russian sides, …
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-lab*
JAEA-Review 2022-042, 67 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to increase the emission intensity of LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) by superimposing MW (microwave) and apply it to uranium isotope measurement. In FY2021, after confirming that there was no problem in terms of specifications including noise leakage by downsizing the semiconductor MW oscillator and evaluating it as a single unit, the possibility of uranium isotope measurement was examined by applying it to the LIBS experiment. In addition, the optimized design of the MW antenna was carried out. By applying them, we confirmed the actual performance, …
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2021 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2022-037, 118 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple
, and X-rays" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, we have established the latest measurement system, such as the multiple  -ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereafter referred to "SDM") was developed. In the study, the
-ray detection methods, and the Spectral Determination Method (hereafter referred to "SDM") was developed. In the study, the  -ray measuring device was installed, and the measurement system consisting of the Ge detector, CeBr
-ray measuring device was installed, and the measurement system consisting of the Ge detector, CeBr detector, and NaI detector was completed in FY2021. In the SDM development, standard spectra of
detector, and NaI detector was completed in FY2021. In the SDM development, standard spectra of  -ray singles, multiple
-ray singles, multiple  -ray measurements, …
-ray measurements, …
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2022-032, 102 Pages, 2022/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted in FY2021. The present study aims to construct a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2021, we mainly worked on improving the base design and technology development that we had worked on in the previous year, and we also prepared for integration experiments.
Yamane, Yuichi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 59(11), p.1331 - 1344, 2022/11
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)The reactivity was estimated from a time profile of neutron count rate or a simulated data in a quasi-steady state after sudden change of reactivity or external neutron source strength. The estimation was based on the equation of power in subcritical quasi-steady state. The purpose of the study is to develop the method of timely reactivity estimation from complicated time profile of neutron count rate. The developed method was applied to the data simulating neutron count rate created by using one-point kinetics code, AGNES, and Poisson-distributed random noise and to the transient subcritical experiment data measured by using TRACY. The result shows that the difference of the estimated and reference value was within about 5% or less for (
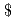
 -1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for
-1) for simulated data and within about 7% or less for 
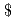
 -1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
-1.4 and -3.1 for the experimental data. It was also shown that the possibility of the reactivity estimation several ten seconds after the status change.
 ,
,  , and X-rays (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project
, and X-rays (Contract research); FY2020 Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development ProjectCollaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Japan Chemical Analysis Center*
JAEA-Review 2021-060, 105 Pages, 2022/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of rapid and sensitive radionuclide analysis method by simultaneous analysis of  ,
,  , and X-rays" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, and develops the measurement system such as multiple
, and X-rays" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to enable rapid analysis of radionuclides in fuel debris and waste, and develops the measurement system such as multiple  -ray detection method. We develop a spectral determination method (SDM method) for integrated analysis by constructing a spectral database for nuclides including
-ray detection method. We develop a spectral determination method (SDM method) for integrated analysis by constructing a spectral database for nuclides including  -rays and X-rays by measurement using this system and radiation simulation calculation. This method enables simultaneous quantification of multiple nuclides and reduces the chemical separation process.
-rays and X-rays by measurement using this system and radiation simulation calculation. This method enables simultaneous quantification of multiple nuclides and reduces the chemical separation process.
 temperature measurement for lamp-based heating device
temperature measurement for lamp-based heating deviceSumita, Takehiro; Sudo, Ayako; Takano, Masahide; Ikeda, Atsushi
Science and Technology of Advanced Materials; Methods (Internet), 2(1), p.50 - 54, 2022/02
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; The University of Tokyo*
JAEA-Review 2021-030, 79 Pages, 2021/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Human resource development related to remote control technology for monitoring inside RPV pedestal during retrieval of fuel debris" conducted in FY2020. This study deals with construction of a monitoring platform for understanding the status inside a reactor during fuel debris removal, and measurement and visualization by sensors moving on the platform. In addition, to develop research personnel through research education by participating in such research projects, classroom lectures, and facility tours is also a goal of this project. In FY2020, the main activities were base design and underlying technology development.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; i-lab*
JAEA-Review 2021-027, 62 Pages, 2021/11
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2020, this report summarizes the research results of the "Challenge to advancement of debris composition and direct isotope measurement by microwave-enhanced LIBS" conducted in FY2020. Although LIBS (laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy) is commercially available for application to remote composition measurement, it is not suitable for high radiation environment due to loss in optical fibers derived from the influence of radiation, reduction in laser transmission output, and nuclear fuel debris properties. There are general concerns of the signal strength decrease. In addition, since LIBS is generally considered to be unsuitable for isotope measurement, there are problems to be improved.
Omori, Takazumi; Otsuka, Kaoru; Endo, Yasuichi; Takeuchi, Tomoaki; Ide, Hiroshi
JAEA-Review 2021-015, 57 Pages, 2021/11
The JMTR reactor facility was selected as a decommissioning one in the Medium/Long-Term Management Plan of JAEA Facilities formulated on April 1, 2017. Therefore, the decommissioning plan was submitted to Nuclear Regulation Authority on September 18, 2019, and the approval was obtained on March 17, 2021 after two amendments. Currently, preparations for decommissioning are underway. The JMTR reactor facility has been aged for more than 50 years since the first criticality in March 1968. However, some of the water piping systems has not been updated since its construction, and there is a possibility of pipe wall thinning due to corrosion, etc. Therefore, the integrity of the water piping was investigated for the facilities that circulate cooling water and pump radioactive liquid waste. In this investigation, the main circulation system of the reactor primary cooling system, the pool canal circulation system, the CF pool circulation system, the drainage system of the liquid waste disposal system, and the hydraulic rabbit irradiation system of the main experimental facility were measured for the pipe wall thickness using the Ultrasonic Thickness Measurement (UTM) method. These values satisfied the technical standards for research and test reactor facilities. No loss of integrity is expected to occur during the upcoming decommissioning period. In the future, we will periodically confirm that there is no wall thinning in the piping of the cooling water circulation and the water transmission system during the decommissioning period by using this result as basic data.
Harada, Masahide; Sakai, Motonobu*; Kurosawa, Takashi*; Haga, Katsuhiro
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 33, p.011098_1 - 011098_5, 2021/03
Materials and Life science experimental Facility (MLF) in J-PARC has a high-intense spallation neutron source and a high-intense muon source induced by 3-GeV and 1MW proton beam. To reduce beam loss, components of proton, neutron and muon beam lines are precisely aligned. However, a settlement of MLF caused by a building construction, installation of heavy shields, earthquakes, consolidation of basement, instrument installation (weight increase), and so on, was assumed in the design stage. Therefore, periodic level measurements in MLF was started from the design stage. A few tens of level measuring points are installed inside and outside MLF. The level measurements were done once per month in the construction stage and per year after operation start. In the construction stage of MLF, it was found that the MLF building largely settled by construction of the building and installation of many shields. And it was also found that The Great East Japan Earthquake on March 11, 2011, caused large settlements of MLF attached buildings. Figure 1 shows fluctuations of measured levels at representative points in each area from December 2011. No critical deterioration (small changes within  1.0 mm) could be detected. However, a few local settlements are found in the MLF building. In the presentation, periodic level measurement results at MLF will be introduced.
1.0 mm) could be detected. However, a few local settlements are found in the MLF building. In the presentation, periodic level measurement results at MLF will be introduced.
Aoki, Katsunori; Yamanaka, Hiroki*; Watanabe, Kazuhiko*; Sugihara, Kozo
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-018, 45 Pages, 2021/02
Mizunami Underground Research Laboratory (MIU) Project is pursued by Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) in the crystalline host rock (granite) as a part of geoscientific study of JAEA, and underground facilities of MIU are constructed down to 500m blow the ground surface. As small amount of Uranium is normally contained in granite, high concentration of radon is sometimes detected in the air of the underground facilities constructed in granitic rocks depending on their ventilation conditions. Radon concentrations in underground facilities of MIU have been measured according to the excavation progress of underground facilities or the change of ventilation system. It is recognized that the data obtained by the actual measurement of radon concentration in such underground facilities are rare and valuable. This repot summarizes the measured data from fiscal 2010 to fiscal 2020, together with the information of ventilation conditions and air temperature which affect radon concentrations in underground facilities. The variation of the equilibrium factors of radon is also examined with the actually measured data. As a result, it has been found that radon concentration in the drift is high in summer and low in winter according to the natural ventilation caused by the seasonal temperature difference between in and out of the underground facilities. Furthermore, the temporary increase in the equilibrium factor of radon in the drift at the start of ventilation is supposed to be due to the aerosol increase by the ventilation flow, such as the dust blown up.